The Cloud Structure of Venus Can Best Be Described as
Are confined to a narrow layer about 60 km above. These are formed by the very rapid photooxidation of carbonyl sulfide in the upper atmosphere.

Life Free Full Text The Case Or Not For Life In The Venusian Clouds Html
The cloud structure in the atmosphere of Venus can be described as.

. Surface temperatures on Venus are about 900 degrees Fahrenheit 475 degrees Celsius hot. The region in which the atmospheric temperature decreases with altitude. The clouds are more opaque near the equator giving Venus a dark band in Akatsuki IR2 images and more transparent lighter toward the poles.
The atmosphere extends to about 250 km above the surface. This altitude difference seems to be one of the main responsible factors in the formation of the so-called cold collar. Venus is closer to the Sun so it gets more intense sunlight Planets cloud-over is highly reflective reflecting 60 of the suns light As seen from Earth the.
Clouds are not located at the same altitude everywhere in Venus atmosphere. The surface of Venus can best be described as. The entire globe of Venus is covered by layers of cloud which extend in height from about 48 to 80 km and which have a key role in the energy balance of the atmosphere and hence in the climate at the surface Bullock and Grinspoon 1996The available data on the physical structure of the clouds show complex layering in the vertical dimension.
According to LCPSPioneer Venus cloud particle spectrometer Knollenberg and Hunten 1980 the particle size distribution in the main cloud deck has up to three modes Esposito et al. There is haze above and below the clouds. The geometric albedo a common measure of reflectivity is the highest of any planet in the Solar System.
Up to 10 cash back Venus clouds consist of fine particles with sizes of up to about 10upmumbox m. It is proposed that the visible cloud deck on Venus is composed of droplets of sulfuric acid. Venus has a thick toxic atmosphere filled with carbon dioxide and its perpetually shrouded in thick yellowish clouds of sulfuric acid that trap heat causing a runaway greenhouse effect.
It may have had water oceans in the past 23 24 but after these evaporated the temperature rose under a runaway greenhouse effect. Venus can be best described with two words. How much does Venuss clouds reflect.
They are 10km lower at the poles than at the equator. A clear layer at the surface a haze layer above it and then a thick layer of permanent cloud. Pioneer Venus measurements showed there to be a layered structure to the Venusian clouds which lie between altitudes of roughly 4560 km within the troposphere of Venus ie.
Nicknamed the Giant Dark Cloud scientists first noticed that feature in data gathered by an infrared camera aboard the Japanese spacecraft Akatsuki which has been orbiting Venus since 2015The. The radius of Venus is. Venusian clouds are thick and are composed mainly 7596 of sulfuric acid droplets.
Both Venus Express and Akatsuki imaged the lower clouds from 47 to 50 kilometers or 29 to 31 miles on Venus nightside and found patterns that are strikingly different from the upper clouds. The sky of Venus is fully covered by thick clouds of sulfuric acid that are located at a height of 45-70 km making it hard to observe the planets surface from Earth-based telescopes and orbiters circling Venus. The clouds are best described as an.
What are the clouds of Venus made of. These clouds are made up mostly of carbon dioxide which has a greenhouse effect keeping in the Suns heat like a giant blanket. Mostly clear sky with occasional thin high clouds and dust B.
A permanent current of cold air encircling a highly variable warm. Its the hottest planet in our solar system even though Mercury is closer to the Sun. Venus is shrouded by an opaque layer of highly reflective clouds of sulfuric acid preventing its surface from being seen from space in light.
Venus clouds dont reflect. The cloud structure in the atmosphere of Venus can be described as a clear layer at the surface a haze layer above it and then a high thick layer of. Venus isnt the only world beyond Earth where scientists have gotten a possible whiff of life.
13 August 2018 Last Updated. They reflect about 75 of the sunlight that falls on them and are completely opaque. The cloud structure in the atmosphere of Venus can be described as _____.
Isolated clouds forming and dissipating all the time with clear sky between them. Researchers announced today Sept. A clear layer at the surface a haze layer above it and then a high thick layer of permanent cloud.
The cloud structure in the atmosphere of venus can be described as A. The sulfuric acid clouds on Venus. As a result Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system.
Composition and Structure of the Visible Clouds Abstract. The dense clouds of Venus are on full display in this ultraviolet image taken by the Pioneer Venus Orbiter on Feb. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Venus has thick pale yellow clouds of carbon dioxide and sulfric acid. The clouds we see on Venus are made up of sulfur dioxide and drops of sulfuric acid. The entire surface of Venus is constantly covered by clouds.
A a clear layer near the surface a haze layer above it and a high thick layer of dense permanent cloud b a permanent and thick cloud layer extending almost to ground level c isolated clouds forming and dissipating all the time with clear sky between them. These clouds obscure the surface of Venus from optical imaging and reflect about 75 of the sunlight that falls on them.

The Morning Star Venus Venus Planets Planet Model
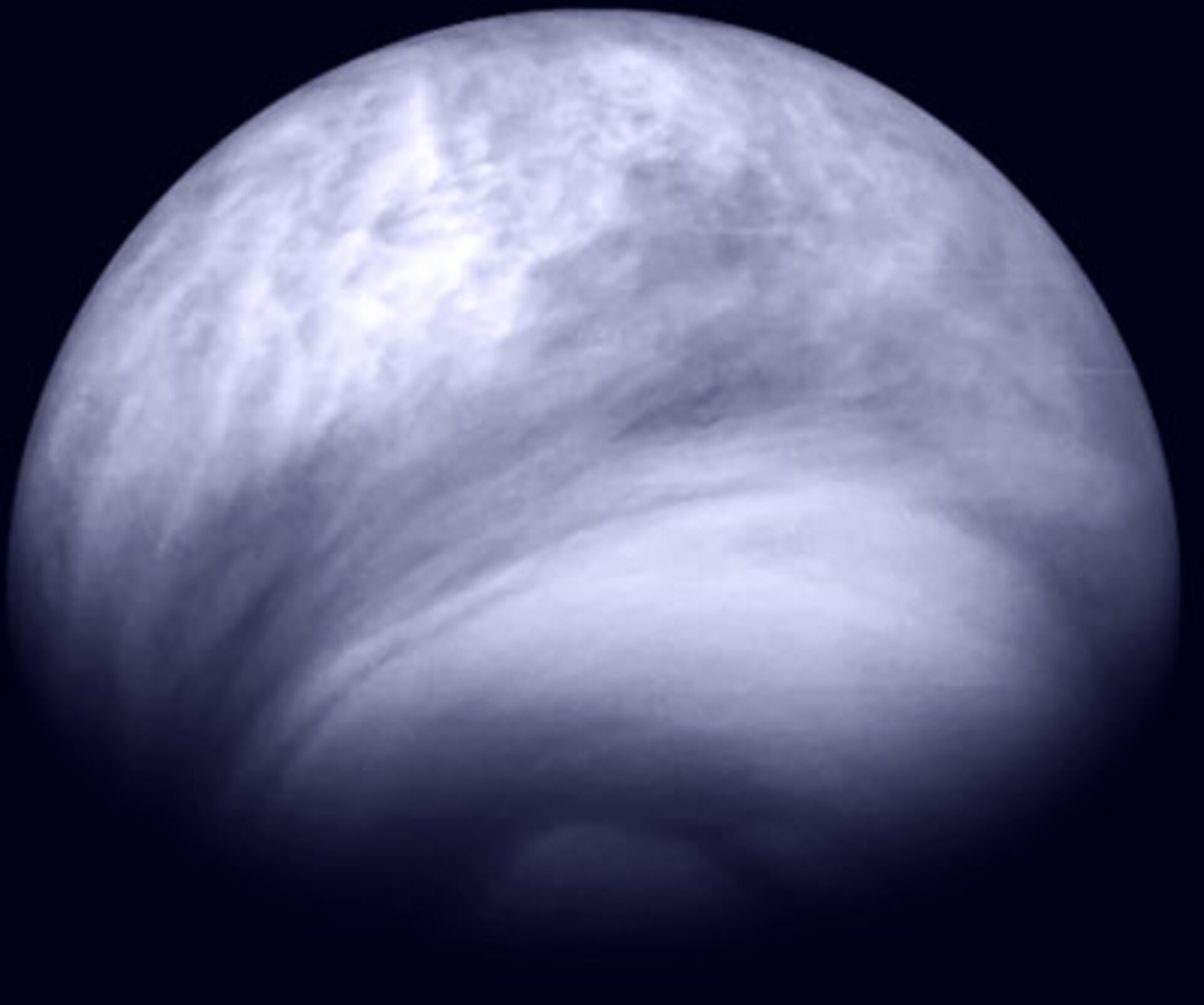

Esa New Details On Venusian Clouds Revealed

Venus Is The Second Planet Closest To The Sun Although Venus Is The Second Planet From The Sun It Is Hotter Than M Solar System Planets Planet Project Planets
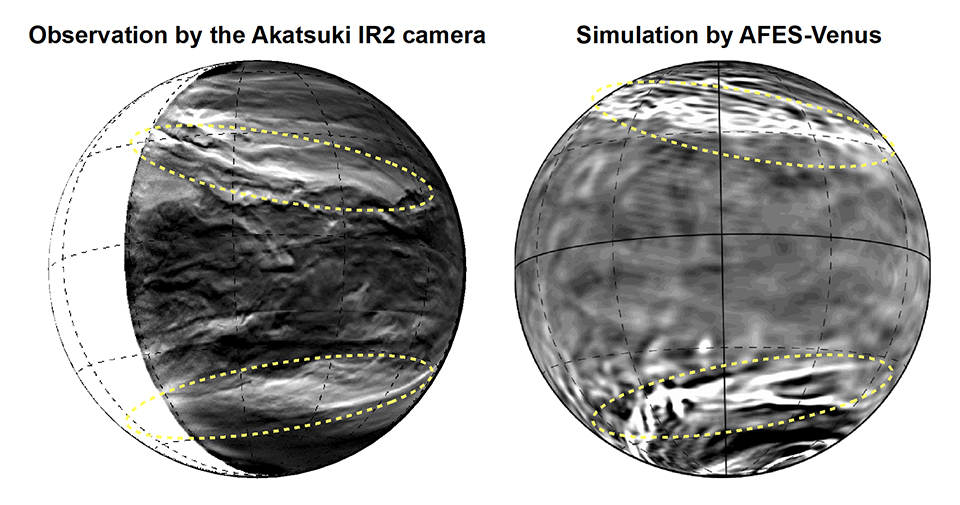
Giant Pattern Discovered In The Clouds Of Venus Nasa Solar System Exploration
Comments
Post a Comment